Climate Change Impacts in Virginia: Climate Cascades
Climate change cascades occur when a species or process not directly affected by changes in temperature or precipitation responds to climate change due to a change in a related species or process that is strongly affected by changes in temperature or precipitation. An example would be a change in the mouse population size, which is indirectly related to changes in precipitation. Although precipitation does not appear to directly affect the mouse population size, it does affect mast production by a number of tree species. The mast is a source of food for the mouse population and when more food is available, a larger population can be sustained.
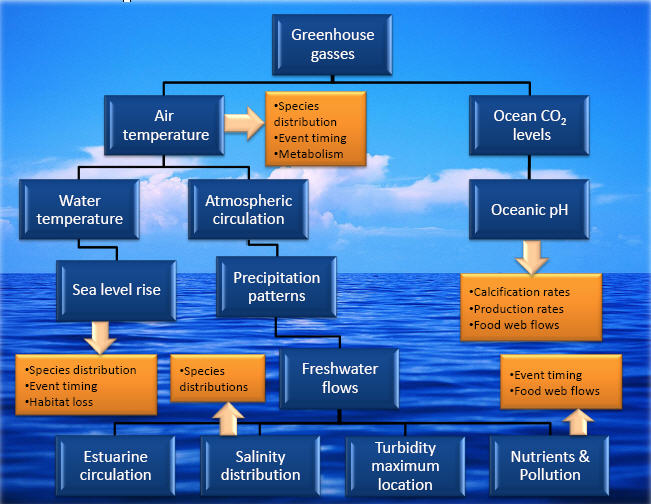
This diagram shows links in abiotic factors that can propagate climate changes. The orange boxes are examples of the types of metabolic and temporal changes that can result from shifts in the abiotic factors. These shifts affect both individual species population dynamics and ecological community make-up and function.
This diagram illustrates ecological connections and how climate changes can resonate through an ecological web.
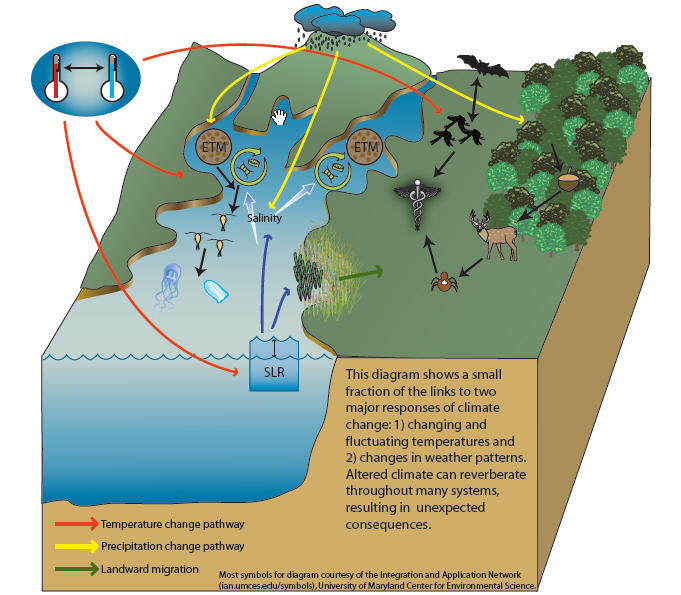
The pathways for the ecological connections include temperature and precipitation changes. The ![]() means 'affects' or 'leads to'.
means 'affects' or 'leads to'.
Temperature Changes Affect:
-
Sea level rise (SLR)
 change salinity distribution
change salinity distribution  Estuarine turbidity maximum (ETM) location
Estuarine turbidity maximum (ETM) location  location of phytoplankton bloom
location of phytoplankton bloom  availability of food for zooplankton population
availability of food for zooplankton population  availability of food for jellyfish and ctenophore populations
availability of food for jellyfish and ctenophore populations -
Phytoplankton bloom timing
 availability of food for zooplankton population
availability of food for zooplankton population  availability of food for jellyfish and ctenophore populations
availability of food for jellyfish and ctenophore populations -
SLR
 marsh location and composition and other landscape features
marsh location and composition and other landscape features -
Mosquito populations
 human health and safety through disease transmission
human health and safety through disease transmission
Precipitation Changes Affect:
-
Salinity and freshwater flows
 ETM location
ETM location  location of phytoplankton bloom
location of phytoplankton bloom  availability of food for zooplankton population
availability of food for zooplankton population  availability of food for jellyfish and ctenophore populations
availability of food for jellyfish and ctenophore populations -
Tree growth and production
 Mast (e.g., acorn) production
Mast (e.g., acorn) production  food availability for deer population
food availability for deer population  tick population size
tick population size  human health and safety through disease transmission
human health and safety through disease transmission -
Bat population
 mosquito population size
mosquito population size  human health and safety through disease transmission
human health and safety through disease transmission