2024 Preliminary SAV Executive Summary
The 2024 distribution of submerged aquatic vegetation (SAV) in Chesapeake Bay and its tributaries was mapped from aerial multispectral digital imagery and satellite imagery. The aerial imagery was acquired between May and October 2024, with a resolution of 24 cm, encompassing 193 flight lines.
Chesapeake BayFor 2024, 33,498 hectares (82,778 acres) of SAV were mapped in Chesapeake Bay and its tributaries. Although the Chesapeake Bay and its tributaries were fully mapped for 2024, due to challenges in acquiring access to the airspace surrounding Washington, DC, imagery was not acquired in 2023 for the upper Potomac River. In order to ensure a valid analysis of change in SAV distribution and abundance with 2023, all direct comparisons to previous years in this report are restricted to only those regions that were mapped in both years. If a region was not mapped in 2023, comparisons are given using area totals from 2022 instead. The area that was not fully mapped in 2023 supported 1,498 hectares of SAV in 2022 (3,703 acres, 4.8% of the Bay total). For 2024, SAV decreased 1% relative to 2023 from 31,963 ha (78,984 ac) in 2023 to 31,747 ha (78,451 ac) in the regions mapped for both years. Due to a number of challenges, additional imagery was acquired from Maxar, SpaceWill, and Planet Labs in order to provide a more complete dataset for Chesapeake Bay. These imagery sources and their locations are detailed below:
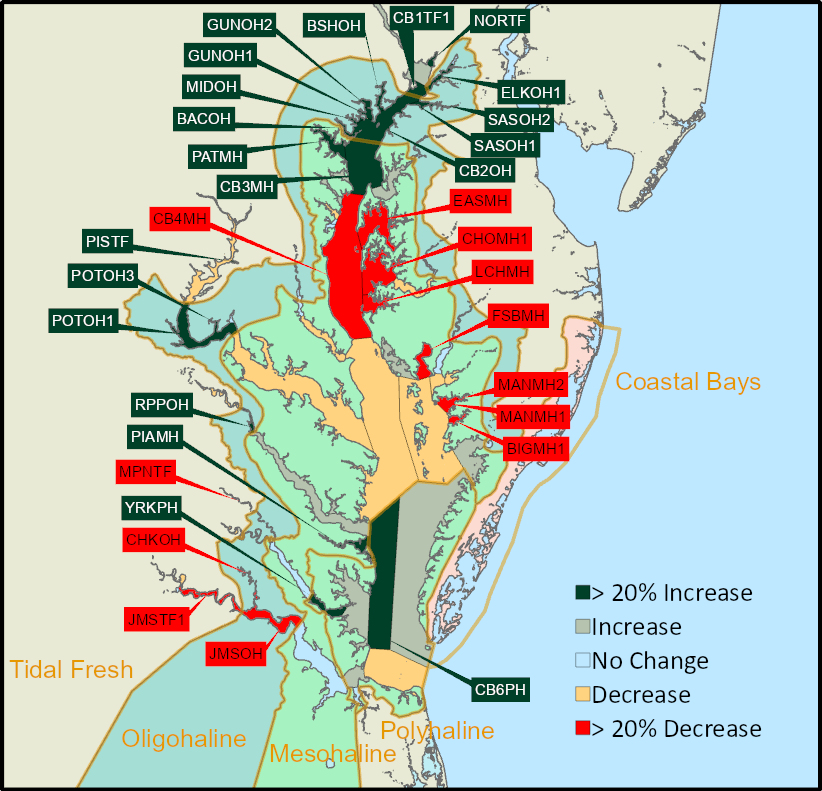
SAV increased in three salinity zones (Tidal Fresh, Oligohaline, and Polyhaline) and decreased in the other salinity zone (Mesohaline). In 2024, SAV increased in 33, decreased in 29, and remained unvegetated in 31 of the 93 CBP segments.
Significant increases and simultaneous decreases in different regions of the bay resulted in little net change in total SAV coverage between 2023 and 2024 (1% decline, -216 hectares, -533 acres). The Polyhaline and Oligohaline zones saw significant increases in SAV, there was a modest increase in the Tidal Fresh zone, and the Mesohaline zone suffered significant declines. The Polyhaline zone increased 14% relative to 2023 (1,212 hectares, 2,996 acres). Segments across the Polyhaline all increased with the largest gains (hectares/acres) occurring in Mobjack Bay, Poquoson Flats, and nearby Western Shore areas. Significantly, this is the most SAV reported in the Polyhaline Zone in the history of the survey, surpassing the previous record set in 1993 by 317 hectares (783 acres). These gains, largely attributable to eelgrass, add to a pattern of consecutive year over year increases in the Polyhaline since the 2019 crash and extension of the meadows into deeper waters. This may indicate improved water clarity in this area of the Bay. The Tidal Fresh Zone was stable, exhibiting a 2% increase (149 hectares, 369 acres) and the Oligohaline Zone showed a 46% increase (584 hectares, 1,442 acres), driven by simultaneous recoveries in multiple areas including the Sassafras, Gunpowder, Back, and Middle Rivers, as well as increases in observed SAV in the Potomac River. In contrast, the Mesohaline underwent a 14% decline (-2,161 hectares, -5,340 acres), which largely occurred along the Eastern Shore of Maryland in the Choptank (-895 hectares, -2,212 acres) and Little Choptank Rivers (-302 hectares, -746 acres) as well as Tangier Sound (-801 hectares, -1,979 acres). The declines in the Choptank mirror measured reductions in water quality within the river, highlighting the strong coupling between water quality and SAV within the Chesapeake Bay, and down-bay declines in Tangier Sound may be connected. These contrasting changes observed throughout the system reflect the incredible diversity of geographic regions, land-use regimes, SAV species, and local environmental conditions that contribute in aggregate to Baywide SAV status each year. |
Tidal Fresh Bay Salinity ZoneIn the Tidal Fresh Bay Zone (19 CBP segments), 8,182 hectares (20,218 ac) of SAV were mapped for 2024. Comparing the same mapped regions between 2023 and 2024, SAV increased 2% from 6,330 hectares (15,641 ac) in 2023 to 6,479 hectares (16,010 ac) in 2024.
Seven of the 19 segments remained unvegetated in 2024. |
Oligohaline Bay Salinity ZoneIn the Oligohaline Bay Zone (25 CBP segments), 1,914 hectares (4,730 ac) of SAV were mapped for 2024. Comparing the same mapped regions between 2023 and 2024, SAV increased 46% from 1,282 hectares (3,168 ac) in 2023 to 1,866 hectares (4,610 ac) in 2024.
|
Mesohaline Bay Salinity ZoneIn the Mesohaline Bay Salinity Zone (41 CBP segments), SAV decreased 14% from 15,528 hectares (38,371 ac) in 2023 to 13,367 hectares (33,031 ac) in 2024.
Fourteen of the 41 segments remained unvegetated in 2024. |
Polyhaline Bay Salinity ZoneIn the Polyhaline Bay Zone (8 CBP segments), SAV increased 14% from 8,823 ha (21,803 ac) in 2023 to 10,036 ha (24,800 ac) in 2024.
None of the 8 segments decreased by at least 20% and by at least 5 ha from 2023 totals. One of the 8 segments remained unvegetated in 2024. |